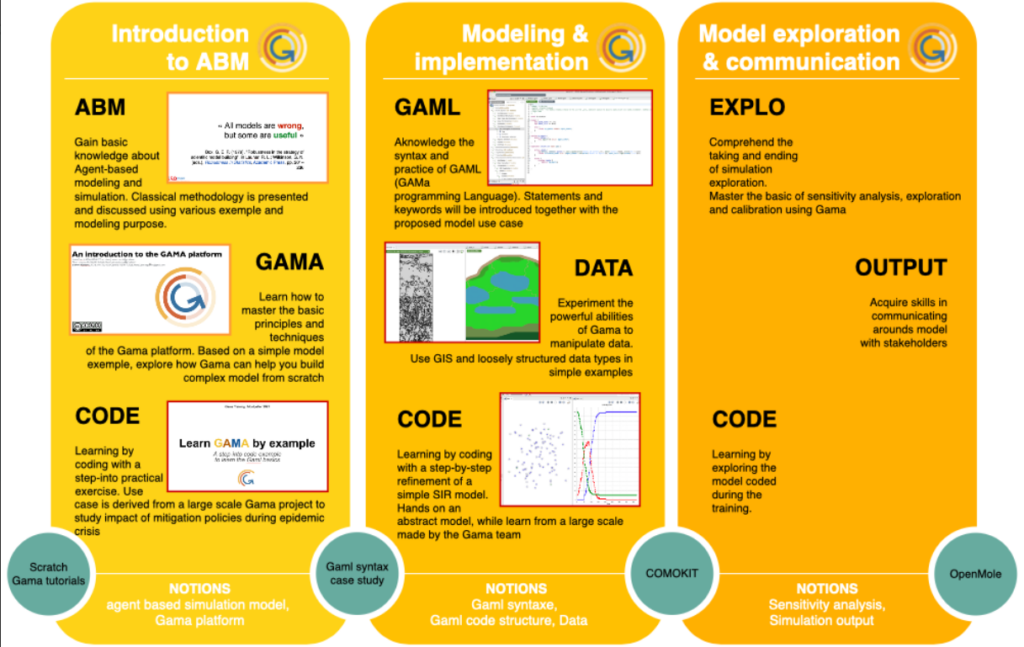
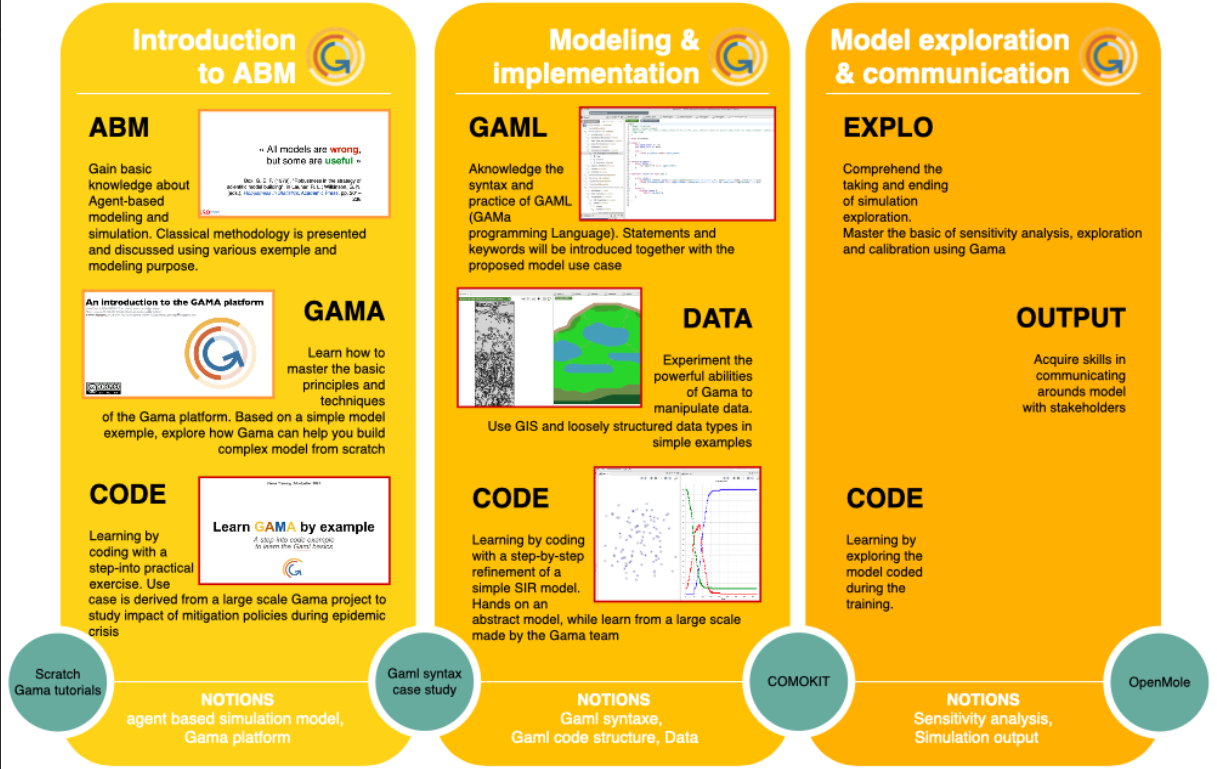
1. What is GAMA? GAMA (GIS Agent-based Modeling Architecture) is an open-source modeling and simulation environment designed for creating spatially explicit Agent-Based Simulations. It allows researchers to build complex models where “agents” (people, vehicles, cells, or environmental elements) interact with each other and their environment.
-
Language: It uses GAML (GAMA Modeling Language), a high-level, intuitive language similar to Java but simplified for non-computer scientists.
-
Core Feature: Its standout capability is the native integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), allowing users to directly import real-world maps (Shapefiles, Raster, OpenStreetMap) to function as the simulation environment.
2. Objective The primary objective of GAMA is to provide a versatile platform that bridges the gap between complex theoretical models and reality. It aims to:
-
Visualize Complexity: Transform abstract data into visual, dynamic simulations (2D and 3D) to observe emergent phenomena.
-
Support Decision Making: Allow planners and researchers to run “what-if” scenarios—such as testing the impact of a new sea dike or evacuation route before implementation.
-
Multi-Scale Modeling: Seamlessly manage interactions at different scales, from individual interactions (micro) to regional dynamics (macro).
3. Training Program Structure Standard training for the GAMA Platform typically covers the following key modules:
-
Module 1: Fundamentals of GAML: Understanding the syntax, defining “Species” (agents), behaviors, and reflexes.
-
Module 2: GIS & Environment: Importing and processing spatial data (GIS integration) to create realistic simulation worlds.
-
Module 3: Visualization & Analysis: creating dashboards, 3D displays, and charts to monitor simulation outputs in real-time.
-
Module 4: Advanced Features: Model coupling (connecting GAMA with Python/AI tools) and designing experiments for stochastic simulation.
4. Applications GAMA is widely used in fields requiring spatial analysis and complex interaction modeling:
-
Urban Planning & Transport: Simulating traffic flow, smart city systems, and pedestrian dynamics.
-
Disaster Risk Management: Modeling evacuation scenarios, flood propagation, and coastal resilience (highly relevant to the Digital Twin proposal).
-
Epidemiology: Tracking disease spread within populations and testing containment strategies.
-
Environment: Modeling ecosystem services, land-use change, and resource management.
5. Time & Logistics
-
Duration: To be updated
-
Location: Online – Offline
-
Prerequisites: Basic programming logic is helpful but not strictly required due to GAML’s intuitive design.
6. Supervisors
- Dr. Huynh Quang Nghi
- Assoc.Prof. Nguyen Ngoc Doanh


Recommended Video Resource Agents, species and logical structure of GAMA This video provides a clear, visual explanation of the fundamental concepts in GAMA (Agents and Species), which is the first step in understanding how to build the models described above.